Selecting Your Cloud Warehouse: When to Choose BigQuery and Redshift
Analytics | January 19, 2026
How architectural choices drive shape cost, control, and scalability in analytics.
Executive Summary
Choosing the right cloud warehouse is a key architectural decision that influences cost, control, and long-term scalability. Google BigQuery and Amazon Redshift both solve enterprise analytics needs, but their architecture shapes how organizations manage data, scale, and optimize spending. This article helps leaders identify when BigQuery offers more agility and when Redshift delivers stronger control, enabling data strategies that support business growth.
Perceptive Analytics POV
In our work, we find that 65% of warehouse performance challenges come from a mismatch between workload patterns and architectural choice. When teams select BigQuery or Redshift based on workload behavior rather than feature lists, they often achieve nearly a 1/3rd reduction in cloud spending. Clients also see analytics delivery move up to 2X faster when warehouse selection aligns with their cloud ecosystem and data gravity.
For CXOs, this raises a direct question.
What warehouse offers the most value for your business model today and at scale tomorrow?
The answer depends less on features and more on how your workloads behave, how your teams operate, and where your data lives.
With this lens, we now break down how BigQuery and Redshift differ across architecture, cost, scalability, sharing, and governance so you can choose with clarity.
Talk with our data warehousing experts. Book a consultation session.
Fig. 1: Warehouse architecture for Amazon Redshift
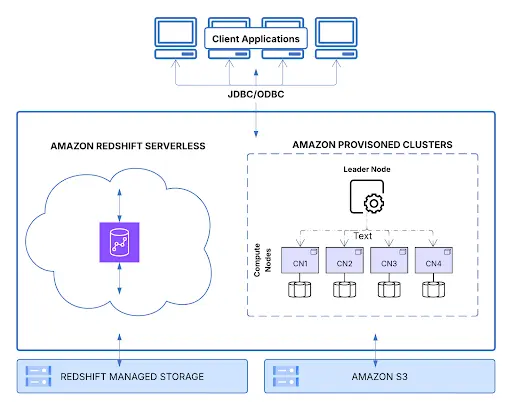
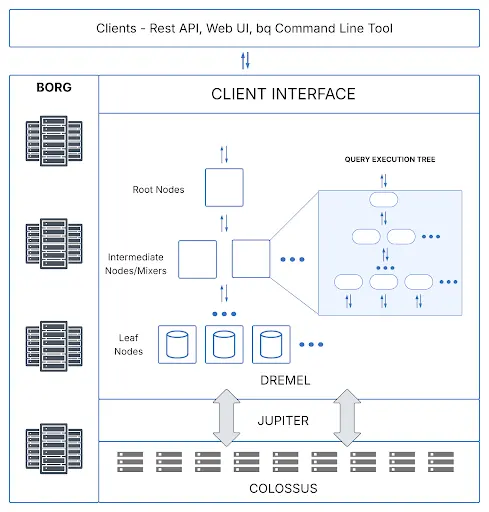
Fig. 2: Warehouse architecture for Google BigQuery
Architectural control models determine operational complexity and responsibilities
Redshift offers deep configurability, giving data engineering teams authority over cluster tuning, workload management, and hands-on performance optimization.
BigQuery’s fully serverless architecture enables rapid deployment and elastic scaling, ideal for teams prioritizing agility over control.
Scaling behavior differs for predictable vs variable workloads
Redshift’s MPP architecture delivers high performance for predictable workloads, allowing teams to tune clusters based on known data patterns.
BigQuery provides dynamic scaling through Colossus storage and the Dremel engine, making it ideal for analytics workloads with high variance.
Data sharing model defines governance and collaboration ease
Redshift supports secure data sharing through Lake Formation and native data sharing, though it requires cross-account IAM setup and may add data transfer costs.
BigQuery enables cross-organization sharing through Analytics Hub, letting teams subscribe to datasets with centralized governance and no data movement.
Support for semi-structured data formats impacts engineering effort and agility
BigQuery handles semi-structured data natively with STRUCT, ARRAY and JSON types, allowing direct querying without complex transformation.
Redshift manages semi-structured data through SUPER columns and Spectrum tables, which need predefined schemas and PartiQL, increasing setup and maintenance effort.
Cost strategy efficiency depends on workload variability and pricing
Redshift supports predictable budgeting through node-based pricing, reserved capacity discounts, and RA3 instances that decouple compute and storage for efficient planning.
BigQuery’s pay-per-query model benefits variable workloads, while flat-rate reservations support large teams with constant query volumes.
Cloud Alignment with the organization’s cloud ecosystem multiplies productivity
Redshift offers deep integration with AWS services like S3, Glue, and QuickSight, making it a strong fit for teams already standardized on the AWS ecosystem.
BigQuery thrives in multi-cloud or data-distributed architectures, especially when paired with BigLake and Omni for cross-cloud analytics.
ML approach balances autonomy with engineering control
Redshift ML works with SageMaker and needs data export and IAM setup but gives strong control over GPU resources and custom model deployment.
BigQuery ML lets analysts build, train, and deploy models in SQL without data movement, supporting fast iteration at scale with no Python skills.
Disaster recovery impacts restoration speed and effort
Redshift depends on the manually configured cross-region snapshots and retention policies. This offers precise control over backup timings but results in long hours to restore data during outages.
BigQuery provides automatic 7-day time-travel recovery with continuous backups. This allows rapid restoration without configuration, although it leads to limited control over backup scheduling.
Ultimate warehouse fit depends on how your teams work and where your data lives
A financial services firm processed terabytes of nightly ETL data. With Redshift tuning and provisioned clusters, batch refresh time dropped from 7 hours to under 3. BI dashboards were consistently ready before business hours, improving planning accuracy by over 18%.
Learn more: How data transformation maturity and observability work together to improve analytics reliability

A tech enterprise stored data across AWS S3, Salesforce, and GCP. BigQuery Omni enabled cross-cloud querying without migration, consolidating reporting within 90 days. This cut data duplication cost by ~30% and accelerated insights for product and sales teams through a unified SQL layer.
Data Warehouse Decision Scorecard
Rate each category from 1 to 5 for your organization. A higher total indicates a better platform fit.
Step 1: Workload and Performance Pattern
Evaluation Criteria | Redshift Score | BigQuery Score |
Workloads are predictable and batch heavy | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐ |
Workloads vary hour to hour or day to day | ⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ |
Need cluster tuning and performance control | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐ |
Need fast start with no infra management | ⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ |
Performance depends on engineering optimization | Strong match | Limited need |
Give Redshift points if you need tuning control. Give BigQuery points if speed, scale, and simplicity matter.
Step 2: Cloud Ecosystem and Data Location
Evaluation Criteria | Redshift Score | BigQuery Score |
Most workloads and data reside in AWS | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐ |
Data lives across clouds and SaaS apps | ⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ |
Uses S3, Glue, SageMaker ecosystem | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐ |
Needs Analytics Hub and cross-org sharing | ⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ |
Unified analytics across platforms | Moderate | Very strong with Omni |
Choose Redshift when AWS gravity is strong. Choose BigQuery when data is distributed or multi-cloud by nature.
Step 3: Cost Strategy and Operating Model
Evaluation Criteria | Redshift Score | BigQuery Score |
You want predictable spending with reservations | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐ |
You prefer pay-per-query consumption | ⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ |
Teams capable of tuning for efficiency | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐ |
Need elastic scale with no capacity planning | ⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ |
Storage compute separation is essential | Strong with RA3 | Native and seamless |
Redshift suits fixed processing and committed spend. BigQuery suits variable usage with cost flexibility.
*How to Decide? Add your scores for each platform across 3 steps.
Conclusion
BigQuery and Redshift both excel, but they win in different contexts. Architecture shapes operational effort. Scaling patterns affect cost. Data sharing, semi-structured handling, ML, and recovery models influence engineering load. No single feature decides the outcome. The scorecard is only a guide. The right answer comes from understanding your workloads, ecosystem, governance needs, and the pace your business wants to move at.
Technical Annexure Available
Download the full comparison matrix covering platform capabilities, performance, cost models, and deployment options.
→ Download the Technical Annexure: BigQuery vs Redshift Feature Matrix
If your data warehouse isn’t performing at the speed or scale your business needs, it’s time to reevaluate.
At Perceptive Analytics, we partner with organizations to optimize their warehousing environments, ensuring faster queries and analytics you can trust to drive decisions.
Talk with our data warehousing experts. Book a consultation session.
